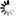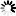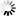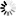FITC标记羧甲基葡聚糖
Trade name: FITC-CM-dextran
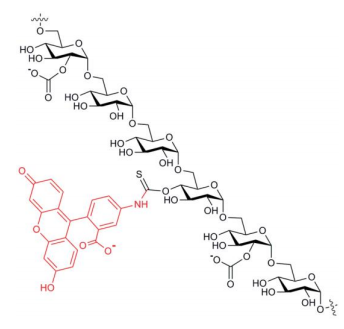
图 1. FITC标记羧甲基葡聚糖的结构式
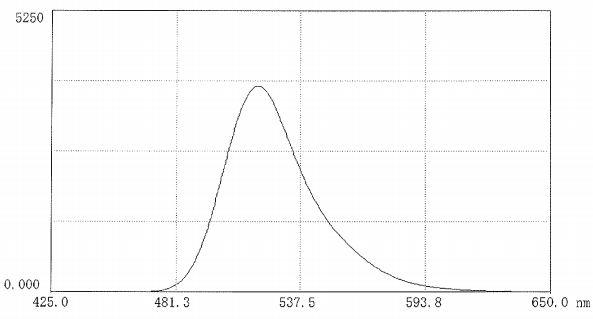
图2. FITC标记羧甲基葡聚糖在0.025M硼酸盐缓冲溶液(10mg溶于50 ml缓冲液pH9.0)的荧光图谱。
激发波长493nm;发射波长519nm
|
产品编号
|
品名
|
分子量(kDa)
|
包装
|
|
FCMD4-100mg
|
FITC-CM-dextran 4
|
4
|
100 mg
|
|
FCMD4-1g
|
1 g
|
||
|
FCMD20-100mg
|
FITC-CM-dextran 20
|
20
|
100 mg
|
|
FCMD20-1g
|
1 g
|
||
|
FCMD40-100mg
|
FITC-CM-dextran 40
|
40
|
100 mg
|
|
FCMD40-1g
|
1 g
|
||
|
FCMD70-100mg
|
FITC-CM-dextran 70
|
70
|
100 mg
|
|
FCMD70-1g
|
1 g
|
||
|
FCMD150-100mg
|
FITC-CM-dextran 150
|
150
|
100 mg
|
|
FCMD150-1g
|
1 g
|
2. K. Gekko and H. Noguchi, Selective interaction of calcium and magnesium ions with ionic dextran derivatives, Carbohydr Res, 69(1979), 323-326.
3. O.Smidsröd and A.Haug, Estimation of the relative stiffness of the molecular chain in polyelectrolytes from measurements of viscosity at different ionic strengths, Biopolymers, 10(1971), 1213-27.
4. P. Rongved and J. Klaveness, Water soluble polysaccharides as carriers of paramagnetic contrast reagents for magnetic resonance imaging; Synthesis and relaxation properties, Carbohydr Res, 214(1991), 315-323.
5. S.W Zheng, M. Huang et al., RGD-conjugated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, J Biomater Appl, 28(2014), 1051-1059.
6. D. Asgiersson, D. Venturoli, B. Rippe and C. Rippe, Increased glomerular permeability to negatively charged polysucrose relative to neutral polysucrose in rats, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 291(2006), F1083-9.
7. C. Martin, E .Dolmazon, K. Moylan et al., A charge neutral tuneable polymersome capable of high biological encapsulation efficiency and cell permeation, Int J Pharmaceutics, 481(2015), 1-8.
 |
 |
 |
| 官网:www.cxbio.com | 微信服务号:iseebio | 微博:seebiobiotech |
 |
 |
 |
| 商城:mall.seebio.cn | 微信订阅号:seebiotech | 泉养堂:www.canmedo.com |
相关资讯
- 25-羟基维生素D-磁微粒化学发光法(AE/AP) /荧光免疫层析解决方案(双抗体夹心法)
- Science解开长期谜题:破译血清素在我们大脑中的作用
- 青刺果油:源自自然的保湿抗衰产品
- 解读诺贝尔生理学或医学奖给人类机体免疫系统研究带来的贡献?
- 血清选购全攻略:教你慧眼识各类优质血清产品
- 国货之光 ——Seebio(R) TEV 蛋白酶(TEV Protease)活性测定试剂盒
- Science:挑战常规!局部的蛋白激酶A在激活期间仍然保持完整
- 蛋白质组学试剂 Proteomic reagents - Lumiprobe其它试剂(1)
- 西宝生物 laysan - 代理证书
- Nature:颠覆常规!揭示细胞产生piRNA新机制
新进产品
同类文章排行
- 汽巴蓝3G-A(Cibacron Blue 3G-A)
- 异硫氰酸荧光素 (FITC)
- TdB染料
- 透明质酸衍生物 Hyaluronic acid derivatives
- 聚蔗糖 Polysucrose
- 季胺标记葡聚糖 Q-Dextran
- 苯基标记葡聚糖 Phenyl-dextran
- 赖氨酸标记葡聚糖 Lysine-Dextran
- 羧甲基标记聚蔗糖 CM-Polysucrose
- 羧甲基标记葡聚糖 CM-Dextran
资讯文章
您的浏览历史